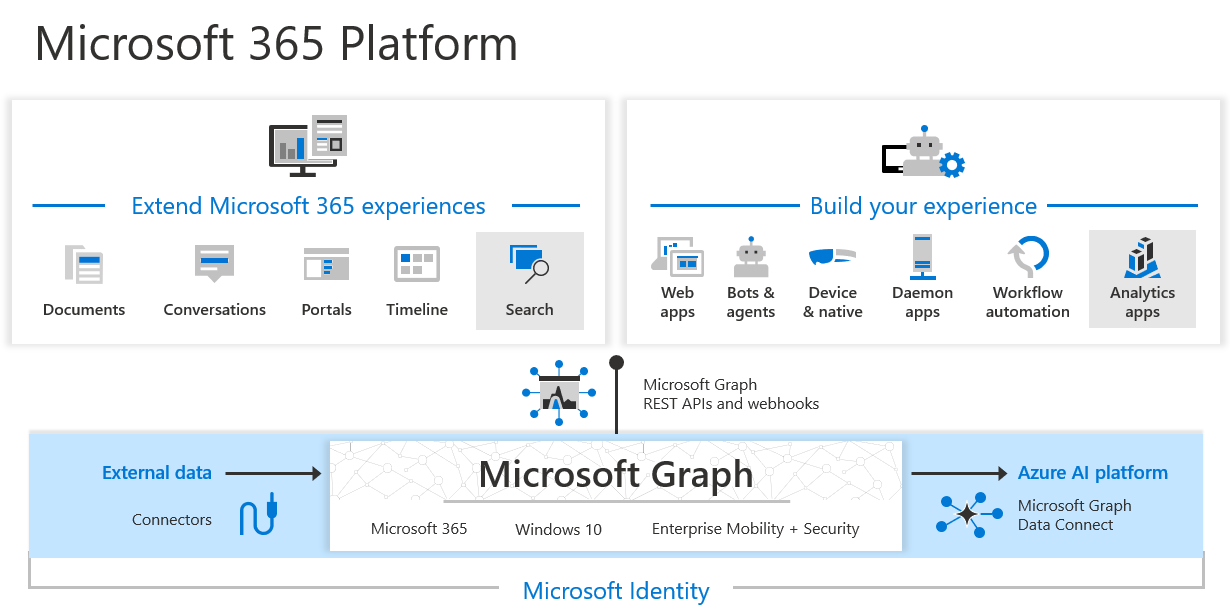
Entra Useless Insights Report
Overview
Yes. The name is snarky on purpose.
With the drive to using phishing-resistant MFA something on the mind of many organizations, I’ve been taking a look at the Usage & Insights Report features in Entra, specifically the Authentication methods activity report.
Enumerating the type of authentication methods registered on a user, on a per-user basis, can be time consuming, and would become untenable in extremely large organizations.
Authentication methods activity reporting to the rescue – right? Not so much.
In digging into the report, whether it’s through the Entra admin center or through Microsoft Graph PowerShell SDK, the data reported through this is just astoundingly awful if you want to try and build some basic measurements around who is actually registered for passkeys (FIDO2); I haven’t looked to see if it’s as awful with other methods.
Luckily in the tenant I’m examining, there are only a few hundred user objects, so it’s also feasible to enumerate each user the long way, which I’ll cover below as the workaround. I’ve posed a complaint to Microsoft in some channels and have yet to hear anything back, other than similar experiences from a few others.